MRI NEWSLETTER: MR of the Bipartite Patella
Posted April 10, 2017
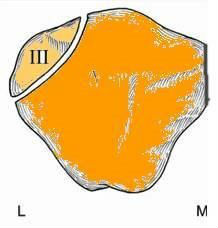
The bipartite patella is a normal patellar variant secondary to failure of fusion. Bipartite patella is often confused with a patellar fracture. Bipartite patella occurs in 8% of the population, is much more common in males 9:1, and bilateral in 50-80%. Bipartite patella occur most commonly in the superior- lateral location, 75% of cases.
Bipartite patella is usually asymptomatic and found incidentally with only 2% symptomatic. In a bipartite patella there is a fibro-cartilaginous synchondrosis between the main patella and the accessory fragment of the knee. Direct trauma or excessive exercise may result in disruption of the fibrocartilaginous zone. The fibrocartilaginous zone cannot heal by bony union and results in persistent pain. The Vastis lateralis with its traction force may contribute to separation of the fragment. A multi -partite or tripartite patella is rarer.
Additional Notes on the Patella:
Patella instability is the most common knee pathology in children resulting from transient lateral patellar dislocation.
Nail-patella syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant condition of nail dysplasia, patellar aplasia-hypoplasia, elbow arthrodysplasia, iliac horns, and proteinuria with 5% progressing to ESRD. Quadriceps tendon rupture is more common than patellar tendon rupture.
The condition is most common in young male athletes and usually secondary to a fall or a kick to the knee. Repetitive injuries such as cycling or hill climbing are less common causes. The condition is aggravated by squatting, jumping, or climbing stairs. The patients complain of the knee giving way. The bipartite patella is often confused with patellar fractures. Compared to the patellar fracture, the bipartite patella is located superior -laterally, has a rounded corner, and may have similar findings on the opposite knee.
On MR examination, the symptomatic bipartite patella has edema of the synchondrosis and bone marrow edema commonly secondary to trauma.
Read the full article here MR of the Bipartite Patella
By Dr. William Renner
